Did you know that a one-second delay in page response can reduce conversions by 7%? In high-stakes AWS environments, latency is a silent budget killer that erodes user experience and inflates cloud spend. To optimize your stack, you must systematically diagnose and eliminate these bottlenecks.
Defining the boundaries of AWS cloud latency
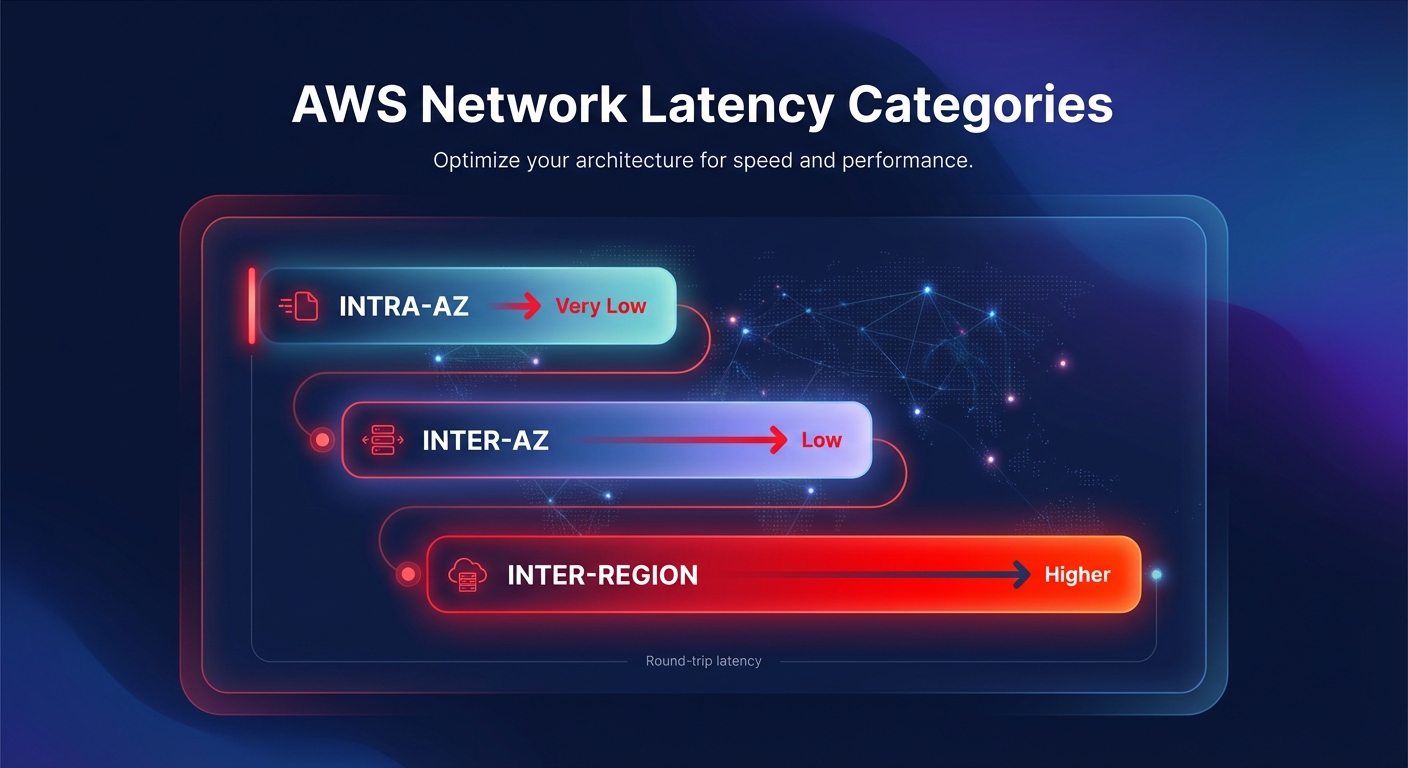
Cloud latency in AWS is the round-trip time required for a data packet to travel between source and destination within the global infrastructure. To optimize your stack, you must differentiate between three primary latency categories. Intra-AZ latency provides the baseline for high-speed performance, often delivering sub-millisecond response times with enhanced networking. Inter-AZ latency typically ranges from 0.250ms to 3.37ms because AWS maintains Availability Zones within 60 miles of each other. Finally, inter-region latency is governed by geographical distance and the speed of light across fiber optics.
Understanding these benchmarks is critical when benchmarking your cloud performance. If your application experiences spikes beyond these baselines, the issue likely resides in architectural patterns, resource configuration, or network congestion rather than the underlying AWS physical infrastructure.
Systematic diagnosis of network bottlenecks
Before you can reduce latency, you must isolate its source using AWS network performance monitoring tools. AWS Network Manager provides real-time visibility into inter-region and inter-AZ latency trends with 45-day historical tracking. Amazon CloudWatch allows you to set granular alarms for application-level performance, while AWS X-Ray is indispensable for distributed microservices. It provides end-to-end tracing that can pinpoint whether a 500ms delay stems from a slow database query, a cold Lambda start, or an inefficient API Gateway integration.
A common pitfall in cloud performance troubleshooting is ignoring “micro-bursts” that saturate instance-level bandwidth. Modern Nitro-based instances support high-throughput networking, but smaller instance types are often throttled. If your EC2 performance tuning efforts are not yielding results, check your volume queue length and network throughput limits to ensure your compute choice is not choking your data transfer.
Architectural patterns for latency reduction
One of the most effective ways to slash network lag is implementing the Availability Zone (AZ) Affinity pattern. By routing traffic so that components within a request chain stay within the same zone, you can achieve a 40% reduction in median network latency compared to distributed architectures. This pattern also serves a dual purpose by significantly reducing cross-AZ data transfer costs, which AWS typically charges in both directions.

For workloads requiring the absolute lowest possible latency, such as high-frequency trading or real-time gaming, you should utilize cluster placement groups. This strategy logically groups instances within a single AZ to minimize physical distance between nodes, pushing performance beyond the standard enhanced networking baseline. Furthermore, utilizing Network Load Balancers (NLB) with AZ DNS affinity ensures that clients favor IP addresses in their own zone, which minimizes unnecessary boundary crossings and reduces tail latency.
Optimizing storage and database response times
Storage latency is frequently the root cause of perceived network lag. When troubleshooting Amazon EBS latency, choosing the right volume type is paramount. While gp3 volumes offer excellent general-purpose performance, mission-critical applications often require the sub-millisecond tail latency of io2 Block Express. If you find your IOPS are hitting a ceiling, following EBS best practices by migrating from gp2 to gp3 can provide more predictable performance while simultaneously reducing costs by roughly 20%.
In the database layer, RDS read replicas can offload heavy read traffic, but asynchronous replication can introduce data lag. For those using MySQL or PostgreSQL, RDS performance tuning often involves adjusting memory allocation and connection pooling. Ensuring that your replica configuration closely matches the primary instance prevents storage bottlenecks from creating replication lag that compromises application responsiveness.
Reducing scaling lag in Kubernetes
For teams running containerized workloads, latency often manifests as scaling lag. This occurs when Kubernetes cannot provision pods or nodes fast enough to handle traffic spikes. You can mitigate this by accelerating your Kubernetes scaling strategies through node pre-warming and the use of placeholder pods. Maintaining a buffer of ready-to-use capacity eliminates the wait for cloud provider node provisioning, ensuring your Kubernetes optimization on AWS results in a snappier user experience.

- Enable image caching by pre-pulling images onto nodes to avoid deployment delays.
- Use lightweight base images like Alpine or Distroless to reduce container startup time.
- Tune the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) to detect load spikes more rapidly by reducing check intervals.
Balancing peak performance with cost-efficiency
Achieving low latency usually comes with a premium price tag, but strategic resource selection can mitigate these costs. Adopting AWS Graviton instances can offer up to 40% better price-performance over comparable x86 instances, providing higher throughput and lower latency for less money. However, the manual effort required to continuously tune instances, volumes, and commitment strategies is immense for most engineering teams.
Hykell removes this burden by providing automated cloud cost optimization that operates on autopilot. While you focus on building architectural patterns like AZ Affinity and edge caching, Hykell works in the background to optimize your AWS rates and right-size your infrastructure without compromising performance. By ensuring your resources are matched precisely to your workload demands, you can reduce your AWS bill by up to 40% while maintaining the low-latency response times your users expect. To see how much you could save while improving your application’s responsiveness, explore our automated observability tools or use our cost savings calculator to audit your current environment.