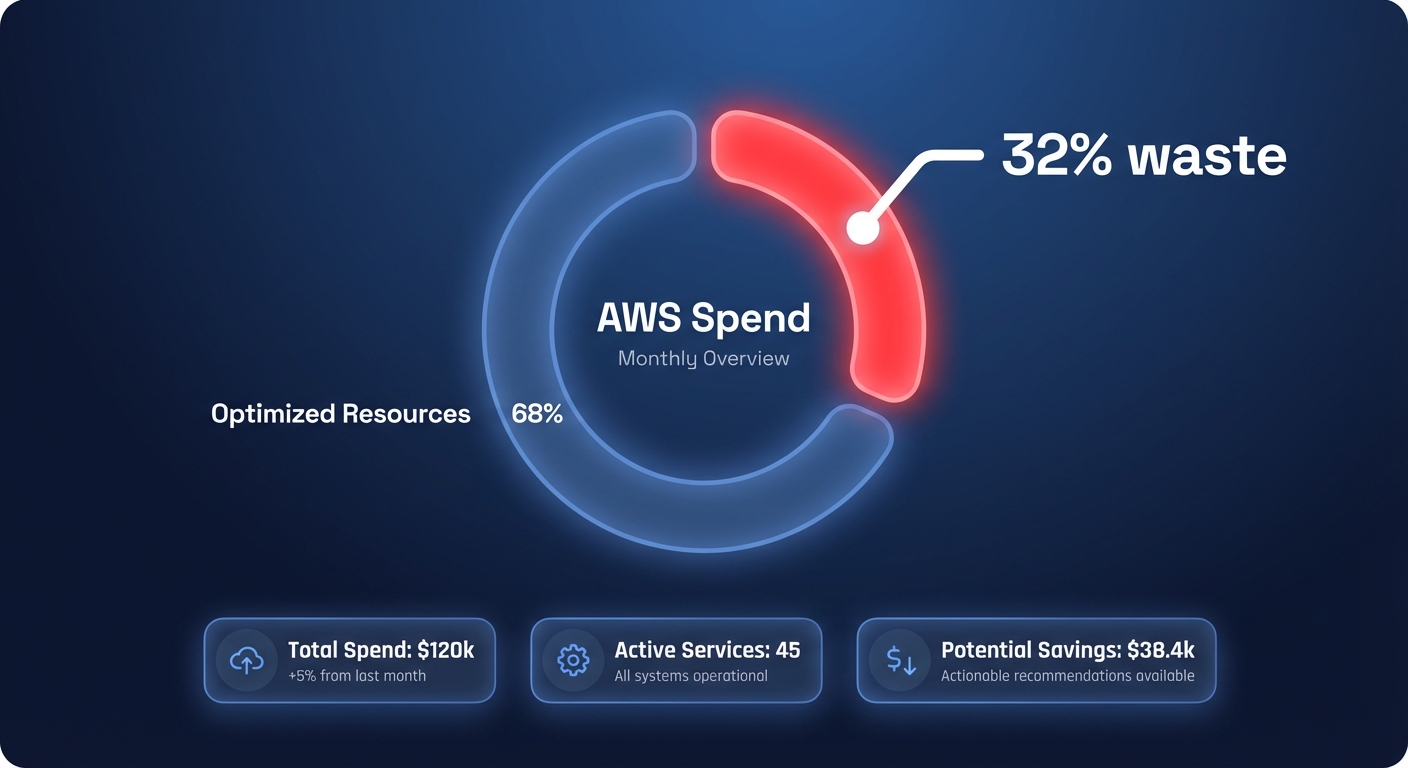
Are you burning $1 for every $3 spent on AWS? Research indicates that organizations waste roughly 32% of their cloud spend on idle resources and over-provisioning. Implementing a systematic cost optimization strategy can recover these margins without sacrificing your application’s performance.
Closing the visibility gap with granular attribution
You cannot optimize what you cannot see. While using AWS Cost Explorer for historical analysis provides a baseline, it often lacks the resource-level granularity required to drive engineering accountability. Statistics show that 54% of cloud waste stems from a lack of visibility into which specific teams or microservices are driving costs. Without clear attribution, engineering leaders struggle to identify where architectural inefficiencies exist.
The first step in any systematic reduction plan is implementing a robust tagging taxonomy for cost allocation. By enforcing tags for Environment, Owner, and CostCenter, you can transition from “unallocated spend” to a clear showback model. This data-driven approach allows you to identify “zombie” resources, such as unattached EBS volumes or forgotten snapshots, which typically account for 15% of total cloud waste. Once these orphaned resources are tagged, they become easy targets for immediate elimination.

Optimizing compute through right-sizing and architecture
Compute is often the largest line item on your monthly bill, and it is where the most significant over-provisioning occurs. Standard strategies for right-sizing AWS resources can reduce compute costs by 30–50% simply by matching instance types to actual performance requirements. Many instances run at under 10% CPU utilization, signifying that the workload could easily be handled by a smaller, cheaper instance.
However, right-sizing is not just about downsizing; it is about choosing the right processor architecture. Migrating workloads to AWS Graviton instances can deliver up to 40% better price-performance compared to standard x86-based instances. For engineering teams, this is one of the most effective ways to lower unit economics without having to re-architect the entire stack. When you combine this migration with a guide for EC2 instance type selection that favors the latest generation, such as moving from M6i to M7g, you unlock compounding savings that improve both speed and your bottom line.
Managing the commitment-flexibility tightrope
AWS offers deep discounts through commitment-based models, often reaching up to 72% off on-demand prices. The challenge for engineering leaders is the “commitment lock-in” that comes with long-term agreements. If your architecture evolves or you migrate to serverless mid-contract, you may find yourself paying for capacity you no longer use. Choosing between AWS Savings Plans and Reserved Instances requires a careful balance of stability and agility.
Effective AWS rate optimization involves blending different commitment types to cover your baseline. You might use Compute Savings Plans for flexible workloads across Fargate and Lambda, while reserving EC2 Instance Savings Plans for stable, regional baselines. To maximize margins, high-growth teams are increasingly turning to automated cloud cost optimization solutions to manage this portfolio. These systems work on autopilot to buy and sell commitments dynamically, ensuring you maintain high Effective Savings Rates without the need for manual intervention.

Reducing hidden networking and storage convenience taxes
Significant waste often hides in architectural choices that favor convenience over cost. Data processing fees are a prime example of a “hidden tax” that can quickly spiral.
- Networking Efficiencies: Standard AWS NAT Gateway cost optimization can yield massive returns. Processing fees often exceed $0.045 per GB, which is expensive for containerized workloads pulling large images. By refactoring your architecture to use VPC Endpoints (PrivateLink), you can reduce these data processing costs by nearly 80%.
- Storage Refinement: Storage spend can be optimized by shifting from gp2 to gp3 volumes, which typically provides a 20% price reduction while allowing you to decouple IOPS from storage size.
- S3 Tiering: Implementing S3 cost optimization lifecycle policies to move aging data into Glacier Instant Retrieval or Deep Archive can reduce storage costs by up to 90%.
Leveraging spot instances for stateless workloads
For fault-tolerant workloads like CI/CD pipelines, batch processing, or development environments, AWS Spot Instances offer the steepest discounts available, often up to 90% off the on-demand rate. While the two-minute termination notice can be intimidating for production-heavy teams, modern orchestration tools make it possible to run large-scale workloads on Spot with high availability. By designing for failure, you can treat compute as a commodity and dramatically reduce the cost per vCPU for non-critical tasks.
Putting your cloud savings on autopilot
The primary barrier to consistent cost reduction is not a lack of knowledge, but a lack of engineering bandwidth. A manual cloud cost audit is merely a snapshot in time; as soon as your team deploys new code or scales a service, that audit becomes obsolete. This is why the industry is moving toward persistent, automated optimization that adapts as fast as your infrastructure does.
Hykell removes the burden of manual tracking by providing comprehensive cloud observability combined with automated remediation. From right-sizing EC2 and EBS to managing complex commitment portfolios, the platform identifies and executes savings opportunities that typically reduce AWS bills by up to 40%. Because the service operates on a performance-based model – taking only a slice of what you actually save – there is no risk to your existing budget.
If you are ready to stop burning 30% of your budget on idle resources, start by using the Hykell savings calculator to see exactly how much you could recover this month.