Are you paying a “convenience tax” for the public cloud that outweighs its actual value? While AWS offers unparalleled agility, the hidden costs of egress and overprovisioning often lead engineering leaders to reconsider the stability and predictable TCO of private infrastructure.
Choosing between public and private cloud deployment is no longer a simple debate over CAPEX versus OPEX. For US-based engineering and FinOps leaders, the decision hinges on the “tipping point” – the moment where the scale of your workload makes the operational overhead of private cloud cheaper and more performant than the variable costs of AWS.
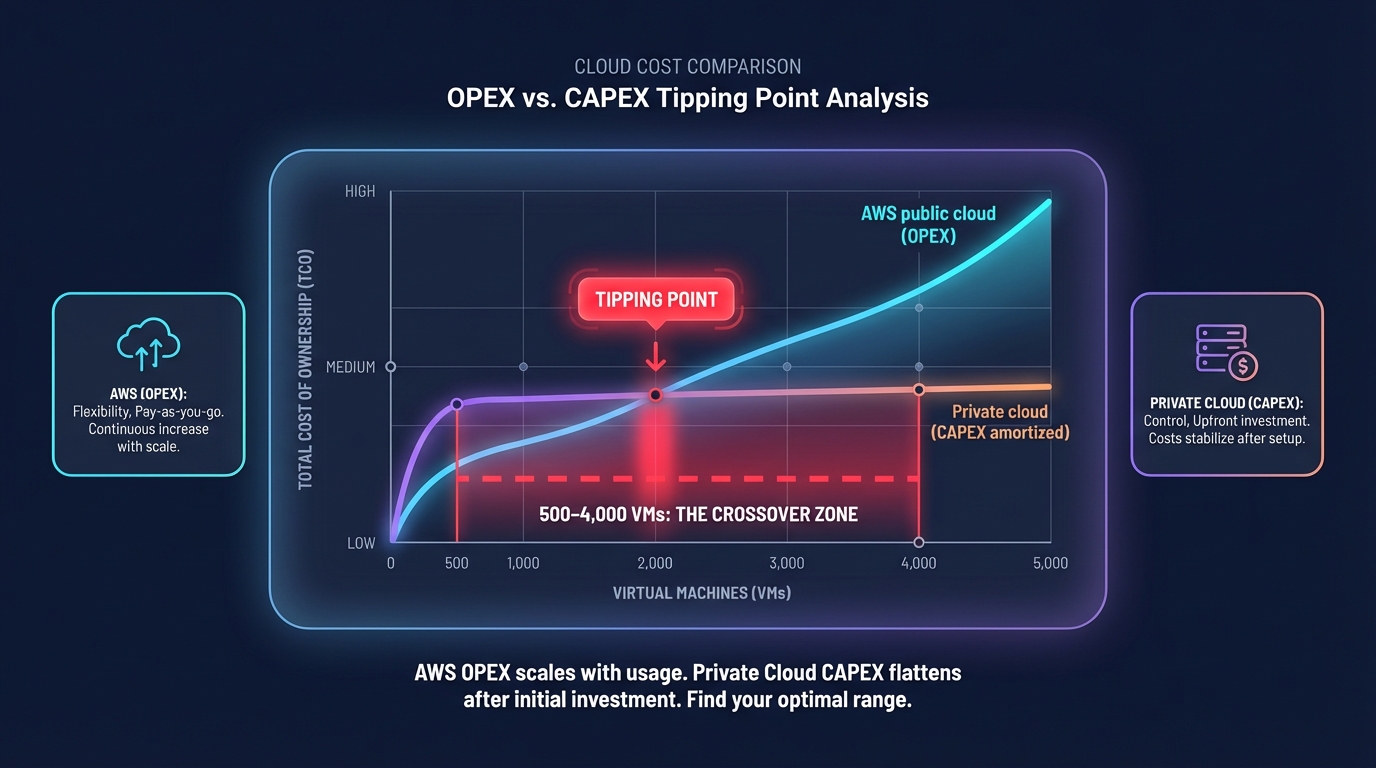
The total cost of ownership: CAPEX vs. OPEX
The primary financial distinction remains the accounting model. Public cloud follows an OPEX model, allowing for rapid experimentation without upfront investment. However, research indicates that at a scale of 500 to 4,000 VMs over a three-year period, private cloud often becomes more cost-efficient because you are not paying the margin for a provider’s managed services.
While private cloud requires significant upfront hardware investment, that hardware is typically amortized over five years, delivering substantial first-year savings once you clear the initial hurdle. In contrast, AWS costs grow linearly – and sometimes exponentially – with scale, particularly for data-heavy or AI-driven workloads. To combat this, many teams conduct a cloud cost audit to identify if their public cloud spend has reached a level that justifies repatriation or if they simply need to eliminate local inefficiencies.
Performance predictability and the “noisy neighbor” effect
Performance in the public cloud is generally excellent, but it is shared. AWS provides robust performance SLAs, often guaranteeing 99.99% uptime for core services. However, latency can be variable due to multi-tenancy, where the activity of other users on the same physical hardware can occasionally impact your throughput.
Private clouds offer a dedicated environment where compute-intensive and mission-critical workloads run without the risk of performance degradation. For adtech, gaming, or high-frequency trading applications where every millisecond counts, the predictability of private hardware often wins. In the public cloud, performance is often tied directly to how you configure your resources. For instance, AWS EBS throughput and IOPS are frequently throttled if not properly provisioned, leading to “performance cliffs” that do not exist in a well-managed private environment where you control the entire storage stack.

Hidden cost drivers in public cloud
The “sticker price” of an EC2 instance is rarely what you end up paying. Public cloud environments are riddled with variable costs that are difficult to forecast, such as AWS egress costs which can account for 25% to 35% of a platform’s total spend. Moving data between availability zones (AZs) typically costs $0.01/GB in each direction, a fee that is entirely absent in a private data center where you own the networking fabric.
Beyond data transfer, engineering teams often “pad” their resource requests to ensure uptime during spikes. This habit leads to a scenario where roughly 40% of EC2 instances run under 10% CPU utilization at peak, resulting in massive waste. Furthermore, selecting the wrong storage class or leaving orphaned snapshots can quietly inflate your monthly bill by thousands of dollars, as these small, unmonitored resources accumulate over time.

Bridging the gap: making public cloud as efficient as private
The flexibility of AWS is hard to give up, especially when your team relies on its vast ecosystem of managed services. To achieve private-cloud-like efficiency without the hardware headache, you can adopt advanced optimization strategies that treat public cloud spend with the same rigor as a physical data center budget.
- Implement rate optimization by moving away from On-Demand pricing. By utilizing Savings Plans and Reserved Instances, you can secure discounts of up to 72% for your steady-state workloads.
- Modernize your architecture by accelerating your Graviton gains. Transitioning to these Arm-based processors can deliver 40% better price-performance compared to traditional x86 instances.
- Enforce continuous resource rightsizing to ensure you only pay for the compute power you actually use. This eliminates the waste margin that typically makes public cloud more expensive than private infrastructure.
Solving the efficiency dilemma
The choice between public and private cloud isn’t binary; it is about finding the most efficient deployment for your specific growth plan. While private clouds offer predictable costs at massive scales, the operational burden of managing physical hardware can distract your engineers from shipping new features.
If you choose to stay on AWS for its scalability and agility, you must ensure your environment is as lean as a private one. Hykell helps you bridge this efficiency gap by automating your AWS rate optimization. We dive deep into your infrastructure to uncover hidden savings and implement strategies that reduce your bill by up to 40%, allowing you to enjoy public cloud flexibility at private cloud price points.
Calculate your potential AWS savings today and see how much you could save on autopilot.