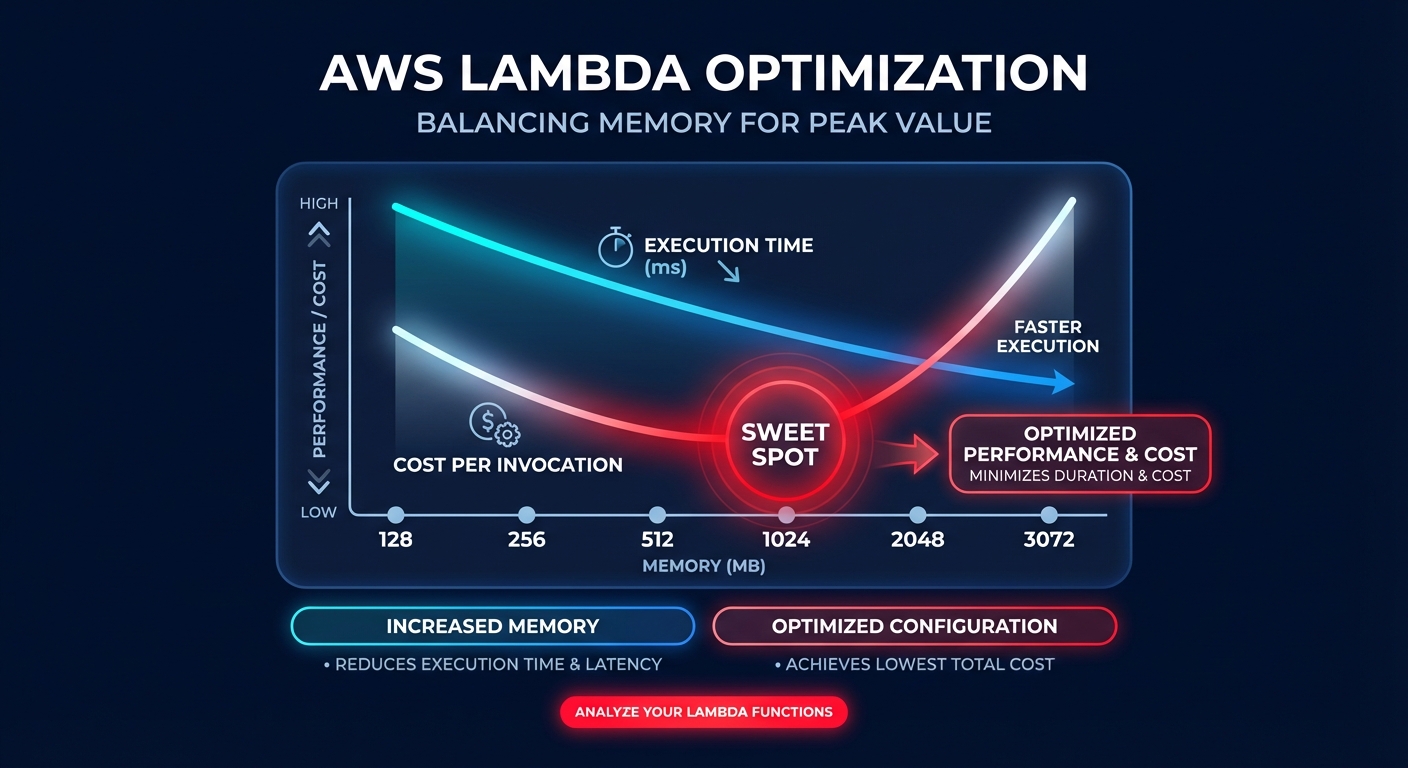
Did you know that increasing your Lambda memory allocation could actually make your function cheaper? Most engineering teams over-provision memory to avoid timeouts, but because CPU power scales linearly with memory, finding the “sweet spot” is the key to mastering serverless FinOps.
In the AWS serverless ecosystem, memory is not just a storage limit; it is the primary lever for compute power. When you adjust the memory slider – which ranges from 128 MB to 10,240 MB – you are directly proportionalizing the CPU cycles and network bandwidth available to that function. Understanding this relationship allows you to move beyond guessing and start right-sizing your cloud resources for maximum efficiency.
The linear relationship between memory and CPU
AWS Lambda allocates CPU power linearly based on your configured memory. At exactly 1,769 MB, a function receives the equivalent of one full vCPU. This means that if you increase memory from 128 MB to 1,024 MB, you are granting your code an 8x increase in processing power. If your workload involves data encryption, image processing, or complex computational logic, this extra horsepower can slash your execution duration enough to lower your total bill.
The billing formula is a simple product of memory and time: Memory (GB) × Duration (seconds) × Price per GB-second. Currently, x86 pricing sits at approximately $0.0000166667 per GB-second. Because of this formula, a function that runs four times faster with four times the memory costs exactly the same as the slower version. However, if that memory increase makes the function five times faster, your total cost per invocation actually drops. Implementing these AWS Lambda cost reduction techniques often reveals that “more expensive” hardware settings lead to cheaper monthly invoices.
Distinguishing between CPU-bound and IO-bound workloads
To optimize effectively, you must identify what is limiting your performance. CPU-bound workloads, such as those performing JSON transformations or complex math, see dramatic duration reductions when you increase memory. In one real-world logistics application, increasing memory from 512 MB to 3,072 MB reduced durations from 15 seconds to just 2 seconds. This change eliminated timeout risks and resulted in a 12% total cost reduction because the extra CPU allowed for faster parallel processing.
Conversely, IO-bound functions that spend most of their time waiting for external API calls or database queries see diminishing returns. If your code is waiting on a legacy SQL server, adding memory won’t make that database respond faster. In these scenarios, sticking to lower tiers like 128 MB to 512 MB is usually the best move. You can pinpoint these bottlenecks by monitoring your application performance to see if duration decreases correlate with memory increases.

A systematic methodology for memory tuning
Optimization is not a one-time event; it must evolve as your code changes. You should begin by establishing a baseline across multiple tiers, such as 128 MB, 512 MB, and 1024 MB, to capture precise execution durations. Once you have this baseline, use AWS CloudWatch application monitoring to track metrics over at least seven days. Pay close attention to the “Max Memory Used” metric. If your maximum usage is consistently under 25% of your allocation and duration is not improving with more memory, you are likely over-provisioned.

Architecture also plays a massive role in your final bill. Migrating to Graviton2 (ARM) instances can provide 20% cost savings over x86 equivalents while maintaining similar performance. Combining this hardware shift with precise memory tuning allows you to hit the peak price-performance point for every microservice in your stack.
Moving from manual audits to automated optimization
While manual benchmarking works for a handful of functions, it fails to scale when you are managing hundreds of microservices. AWS Compute Optimizer can provide recommendations based on 14 days of history, but these are often “point-in-time” fixes that become outdated as your traffic patterns shift or your code evolves. To maintain a truly lean infrastructure, you need a way to analyze and adjust workloads in real-time without constant engineering intervention.
This is where automated platforms like Hykell transform your operations. Instead of burdening your engineers with manual benchmarking, Hykell operates on autopilot to automatically implement optimizations across your compute, storage, and networking layers. By continuously monitoring your environment, Hykell ensures your Lambda functions are always right-sized, often reducing total AWS costs by up to 40% while ensuring full compliance and performance.
Fine-tuning your Lambda memory is one of the highest-impact strategies for modern FinOps teams. By shifting from a “set and forget” mentality to a data-driven approach, you ensure your serverless architecture remains an asset rather than a growing liability. If you are ready to see exactly where your infrastructure is leaking money, Hykell’s detailed cost audits can uncover hidden savings across your entire environment. Under the Hykell pricing model, you only pay a percentage of the actual savings achieved – meaning if you don’t save money, you don’t pay.