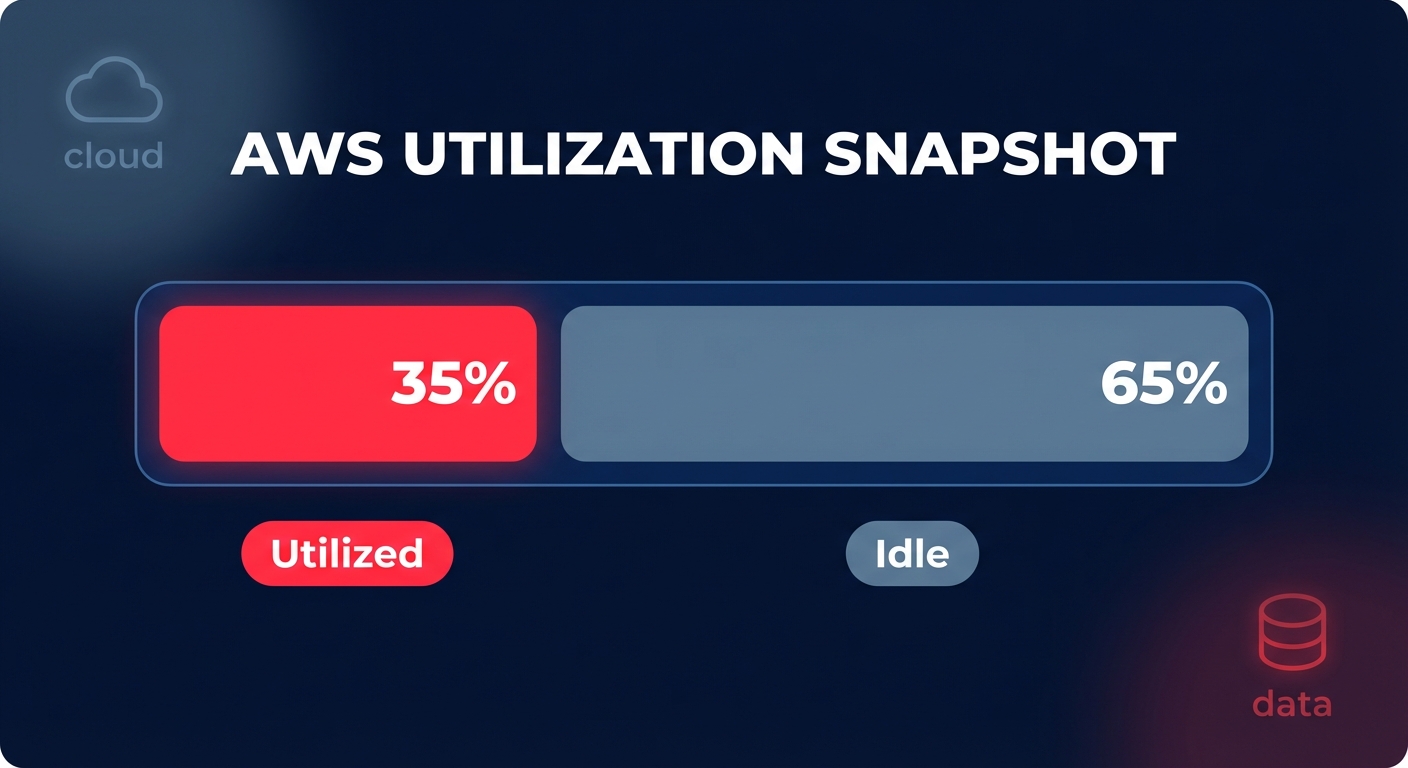
Did you know most AWS environments run at just 30–40% utilization? This means nearly two-thirds of your cloud budget pays for idle silence. Automatic scaling is the essential lever to close this gap and align your spend with real-time demand.
Understanding the AWS scaling ecosystem
While “auto scaling” is often used as a catch-all term, AWS provides several distinct mechanisms to handle demand. Choosing the right one depends on whether you are managing raw virtual machines, containerized tasks, or a complex multi-tier architecture.
EC2 Auto Scaling is the foundation for managing Amazon EC2 instances. It uses Auto Scaling Groups (ASGs) to ensure you have the correct number of instances running to handle the load of your application. In contrast, ECS Service Auto Scaling adjusts the number of containerized tasks in an Amazon ECS service based on CloudWatch metrics like CPU or memory utilization.
For teams managing complex applications that span multiple services, the AWS Auto Scaling unified interface acts as a coordinator. It allows you to manage scaling for EC2, ECS, DynamoDB, and Aurora replicas from a single console. This ensures that your front-end web servers, database read capacity, and application processing layers scale in sync to prevent bottlenecks. When deciding on an orchestration layer, understanding the nuances of EKS vs ECS is vital, as each service handles the transition from task scaling to underlying node scaling differently.
Choosing the right scaling policy for your workload
The success of your scaling strategy hinges on the policy you select. Most engineering teams default to basic thresholds, but modern AWS capabilities allow for much more sophisticated approaches. You should select a policy that matches your traffic profile to avoid the common pitfalls of reactive lag.

- Target tracking scaling: This is the “hands-off” approach that Hykell recommends for most web and API services. You set a target metric – such as 50% average CPU utilization – and AWS handles the math to keep it there. This method can reduce over-provisioning by up to 40% by reacting dynamically to traffic shifts.
- Step scaling: This offers granular control by allowing you to define multiple thresholds. For instance, you might add one instance when CPU hits 70% and three more when it hits 90%, providing a more aggressive response to sudden spikes.
- Scheduled scaling: If you have predictable traffic patterns, such as a retail site that spikes every Friday morning, you can proactively raise your minimum capacity before the load arrives.
- Predictive scaling: By analyzing 14 days of historical data with machine learning, AWS can forecast demand and launch instances ahead of time. This is particularly effective for stable daily or weekly patterns where reactive scaling might be too slow to handle a sudden surge.
For a deeper dive into how to align these policies with your infrastructure, see our comprehensive guide on AWS EC2 auto scaling best practices.
Configuration steps for peak efficiency
Setting up an Auto Scaling Group requires three core components: a Launch Template, an Auto Scaling Group, and a Scaling Policy. You should prioritize the use of launch templates over legacy Launch Configurations. Templates are more versatile, allowing you to mix multiple instance types and purchase models, such as Spot and On-Demand, within a single group to maximize availability and cost savings.
When configuring your ASG, pay close attention to the Health Check Grace Period. If this is set too short, AWS might terminate an instance while it is still initializing, causing a “death spiral” of failed launches. Conversely, the Default Cooldown Period – often set to 300 seconds by default – is frequently too long for scale-in policies. Shortening this period prevents unnecessary costs by terminating idle instances sooner once traffic has subsided.
High availability should also be a primary configuration goal. You should always distribute your instances across multiple Availability Zones (AZs). AWS automatically balances capacity across these zones, which protects your application from localized outages without requiring manual intervention or complex re-routing logic.
Scaling is only half the cost equation
Automatic scaling handles the number of resources you use, but it doesn’t automatically ensure you are paying the lowest price for those resources. To achieve a total AWS cost reduction of up to 40%, you must combine scaling with right-sizing and rate optimization. Scaling an oversized instance still results in waste because you are simply multiplying an inefficient baseline.

Before locking in your scaling policies, use tools like AWS CloudWatch application monitoring to analyze performance. If your instances are consistently running at 10% CPU at peak, you should right-size to a smaller family or accelerate your Graviton gains by migrating to Arm-based processors. These custom AWS chips can cut compute costs by another 20% while providing better price-performance than comparable x86 instances.
Furthermore, integrating Spot instances into your Auto Scaling Groups can provide up to 90% savings for fault-tolerant workloads. By using a mixed-instance policy, you can maintain a baseline of On-Demand instances or Savings Plans while using Spot for the “burst” capacity that handles peak traffic surges.
Advancing to containerized scaling
If you are using ECS or EKS, your scaling strategy becomes two-tiered. You must scale both the pods or tasks and the underlying cluster nodes. For ECS, using Fargate simplifies this significantly by removing the need to manage EC2 instances entirely. Fargate scales per-second based on requested CPU and memory, making it ideal for bursty or unpredictable workloads.
However, for steady-state workloads, AWS Fargate cost optimization strategies often suggest that ECS on EC2 remains more cost-effective when paired with Reserved Instances or Savings Plans. The key is to use Capacity Providers to bridge the gap between your container requirements and the underlying infrastructure. This ensures that the ASG launches the exact amount of compute needed to house your tasks, preventing the “uncovered spend” that often plagues unoptimized clusters.
Whether you are fine-tuning EC2 groups or managing serverless containers, the goal remains the same: matching capacity to demand with surgical precision. Most engineering teams struggle to maintain this balance manually because workload needs change faster than humans can audit them.
Hykell bridges this gap by providing automated AWS rightsizing and AWS rate optimization on autopilot. We dive deep into your infrastructure to uncover hidden savings and implement them without any engineering lift. If you’re ready to see how much your current scaling strategy is leaving on the table, use our AWS pricing calculator guide to estimate your potential or book a free cost audit with Hykell today. We only take a slice of what we save you – if you don’t save, you don’t pay.