Are you still paying for idle time in a serverless environment? While Lambda is billed by execution, misconfigured memory or inefficient event routing can inflate your bill by 300% without adding user value. At scale, these inefficiencies become a primary driver of cloud waste.
Engineering leaders often view Lambda as a “set it and forget it” service, but high-volume workloads require active management to remain cost-effective. To achieve meaningful savings, you must move beyond basic rightsizing and look into the interplay between architecture, runtime performance, and precision-engineered AWS rate optimization.
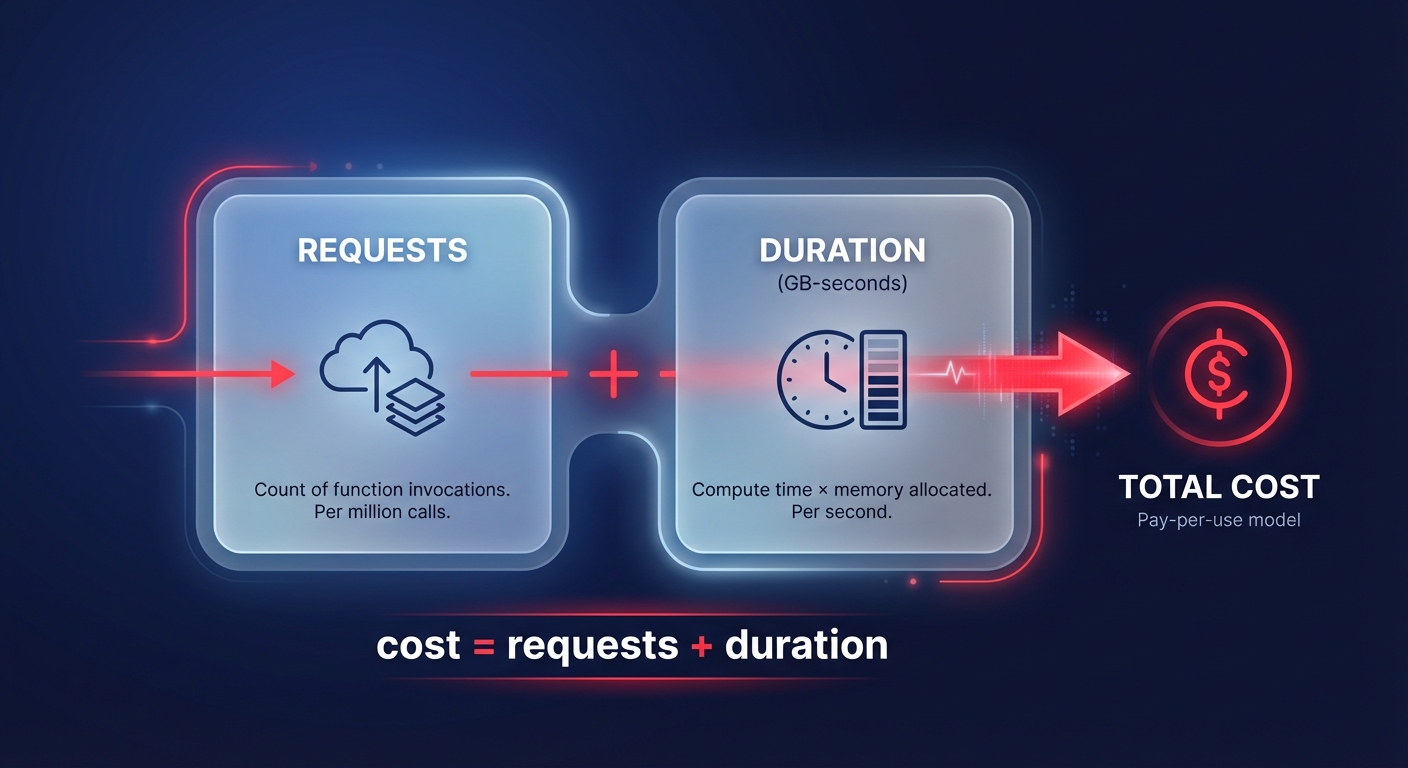
The math behind the Lambda bill
To optimize your spend, you first need to understand the two-dimensional nature of Lambda pricing. AWS charges based on the number of requests and the duration of the execution, which is measured in GB-seconds.
- Request pricing: AWS bills $0.20 per 1 million requests. While this seems negligible, high-frequency event-driven architectures – such as those processing millions of sensor pings or clickstream events – can see request costs rival execution costs.
- Duration pricing: This is calculated by multiplying your allocated memory (in GB) by the execution time (in seconds). AWS bills in 1-millisecond increments. For the standard x86 architecture, the price is approximately $0.0000166667 per GB-second.
A critical nuance often missed by DevOps teams is that memory allocation is the primary resource knob for CPU and network performance. At 1,769 MB of memory, a function receives the equivalent of one full vCPU. Because CPU power scales linearly with memory, increasing your allocation doesn’t just give you more RAM; it provides more processing cycles. This can actually lower costs by reducing the execution duration for CPU-bound tasks.
Technical strategies for Lambda cost reduction
Many teams default to the minimum memory settings to save money, but this often leads to the “power-tuning paradox” where under-provisioned functions run significantly longer, increasing the total bill. For instance, an e-commerce order processing function moved from 256 MB (taking 400 ms) to 1024 MB (taking only 80 ms). This change yielded a 22% total cost reduction per invocation because the 5x speedup more than offset the higher per-millisecond price.

To find the “sweet spot” where the cost-duration curve is at its lowest point, you should utilize tools like leveraging AWS Compute Optimizer to analyze historical performance. For more detail on finding this equilibrium, see our guide on how to choose and tune Lambda memory.
Beyond memory tuning, migrating your functions from x86 to ARM-based Graviton2 processors is one of the fastest ways to secure an immediate 20% discount on duration costs. Most functions using modern runtimes like Node.js, Python, or Java require zero code changes for this migration.
Architecture choices also play a massive role in spend. You can further reduce invocations through:
- Event filtering: Configure filter patterns on the event source mapping so your Lambda only triggers when specific conditions are met, preventing the function from running just to discard a message.
- Batching: Increase the batch size and window for SQS or Kinesis triggers. Processing 100 records in a single 2-second invocation is significantly cheaper than 100 separate 100-millisecond invocations due to the reduction in fixed initialization overhead.
- VPC endpoint utilization: If your function must access private resources, use VPC Endpoints for S3 or DynamoDB to keep traffic within the AWS network and avoid NAT Gateway charges, which can quietly double a serverless bill.
Advanced FinOps workflows for serverless
To maintain these savings, FinOps practitioners must integrate serverless costs into their broader cloud cost budgeting and forecasting workflows. Lambda is eligible for Compute Savings Plans, which offer up to a 17% discount in exchange for a consistent hourly spend commitment. However, because serverless usage is often spiky, committing to peak usage is a common mistake. A more effective strategy involves blending Savings Plans to cover your baseline while using on-demand capacity for bursts.

Observability is another area where costs frequently spiral. CloudWatch logs can represent up to 30% of an engineering team’s monthly bill, particularly when functions use verbose debug logging in production. You can mitigate this by setting aggressive retention policies rather than leaving log groups at the default “Never Expire” setting. Additionally, understanding CloudWatch Logs pricing can help you transition from raw log storage to using metric filters, which extract KPIs and allow you to expire raw logs more quickly.
Finally, because Lambda scales automatically, code bugs like recursive loops can cause massive cost spikes within hours. Implementing automated cost anomaly detection specifically for the Lambda service provides an essential safety net, alerting you to deviations from historical patterns before they impact your monthly invoice.
Operationalizing serverless optimization with Hykell
Manual tuning is a losing battle when managing hundreds of functions across multiple regions. Hykell provides an AWS Cost Optimization Hub that continuously monitors your Lambda environment to identify rightsizing opportunities and architecture inefficiencies.
By combining real-time cloud observability with automated commitment management, Hykell helps engineering teams reduce their total AWS spend by up to 40% without requiring ongoing internal engineering effort. We handle the complexity of rightsizing and rate optimization on autopilot, allowing your developers to focus on building features rather than auditing line items.
Stop overpaying for your serverless infrastructure and start operating with precision. You can calculate your potential savings today or schedule a deep-dive audit to see how Hykell optimizes your Lambda spend with zero financial risk.